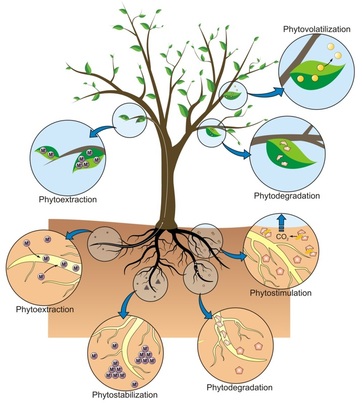
Phytoremediation
It is defined as the treatment of environmental problems (bioremediation) through the use of plants that mitigate the environmental problem without the need to excavate the contaminant material and dispose of it elsewhere.
Phytoremediation consists of mitigating pollutant concentrations in contaminated soils, water, or air, with plants able to contain, degrade, or eliminate metals, pesticides, solvents,explosives, crude oil and its derivatives, and various other contaminants from the media that contain them.
Phytoremediation consists of mitigating pollutant concentrations in contaminated soils, water, or air, with plants able to contain, degrade, or eliminate metals, pesticides, solvents,explosives, crude oil and its derivatives, and various other contaminants from the media that contain them.
A range of processes mediated by plants are useful in treating environmental problems:
- Phytoextraction — uptake and concentration of substances from the environment into the plant biomass.
- Phytostabilization — reducing the mobility of substances in the environment, for example, by limiting the leaching of substances from the soil.
- Phytotransformation — chemical modification of environmental substances as a direct result of plant metabolism, often resulting in their inactivation, degradation (phytodegradation), or immobilization (phytostabilization).
- Phytostimulation — enhancement of soil microbial activity for the degradation of contaminants, typically by organisms that associate with roots. This process is also known as rhizosphere degradation.
- Phytovolatilization — removal of substances from soil or water with release into the air, sometimes as a result of phytotransformation to more volatile and/or less polluting substances.
- Rhizofiltration — filtering water through a mass of roots to remove toxic substances or excess nutrients. The pollutants remain absorbed in or adsorbed to the roots.
You can watch the video about phytoremediation.